Overview
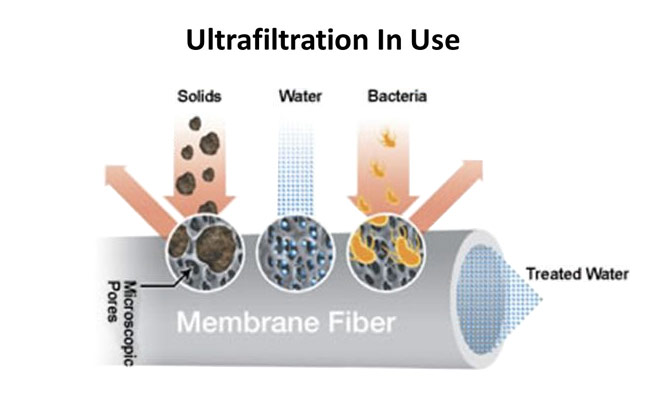
Ultrafiltration (UF) is a variety of membrane filtration in which forces like pressure or concentration gradients lead to a separation through a semipermeable membrane. Suspended solids and solutes of high molecular weight are retained in the so-called retentate, while water and low molecular weight solutes pass through the membrane in the permeate.
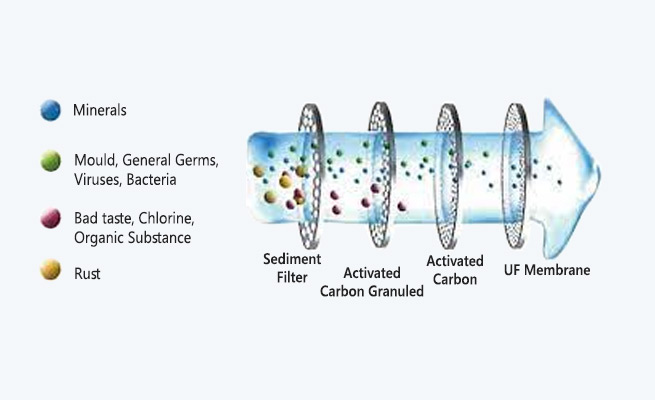
Applications of ultrafiltration UF can be used for removal of particulates and macromolecules from raw water, to produce potable water. It has been used to either replace existing secondary (coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation) and tertiary filtration (sand filtration and chlorination) systems employed in water-treatment plants or as standalone systems in isolated regions with growing populations. When treating water with high suspended solids, UF is often integrated into the process, using primary (screening, flotation and filtration) and some secondary treatments as pre-treatment stages.
Advantages of Ultrafiltration (UF)
- Chemicals required (aside from cleaning)
- Constant product quality regardless of feed quality
- Compact plant size
- Capable of exceeding regulatory standards of water quality, achieving 90-100% pathogen removal.
- Ultrafiltration (UF) processes are currently limited by the high cost incurred due to membrane fouling and replacement.
Please leave a message for more details and we will get back to you soon.
Enquire Now
- Customer Care Services
+1800-103-1145
- Talk to Us